Chaos Hearing
On Listening and Duets: Hearing Performance, Chaotic Dynamics, and Computational Auditory Scenery Analysis
This first project ("On Listening and Duets") and the entire Chaos Hearing project have been started because of a deep appreciation of mathematics, music, and sound. The Chaos Hearing project's goal is to facilitate the conversations between these entities (sound, music, and math. These conversations are between student and teacher, artist and artist, mathematician and mathematician, and artist and mathematician. During the conversations, expect discussions on related research, theories, art, design, and everything else from a formal and wonderfully artistic perspective.
Examples of Theory
We use latex to specify mathematical formulations:
% The normal form equation for the supercritical Hopf bifurication w/ AWGN: n_z(t)
\begin{align}
\dfrac{dz(t)}{dt} = (\mu i\omega_0)z(t) - (a + i/3)|z(t)|^2z(t) + n_{z}(t)
\end{align}
Examples of Code
We use python, matlab, R, swift, and various other programming languages for implementations of theory.
Deep Learning in Swift (Iris ANN, The Hello World of DL)
The Iris genus entails about 300 species, but our program will only classify the following three:
- Iris setosa
- Iris virginica
- Iris versicolor

|
|
Figure 1. Iris setosa (by Radomil, CC BY-SA 3.0), Iris versicolor, (by Dlanglois, CC BY-SA 3.0), and Iris virginica (by Frank Mayfield, CC BY-SA 2.0). |
🧠 Creating a neural network model to classify flowers
|
|
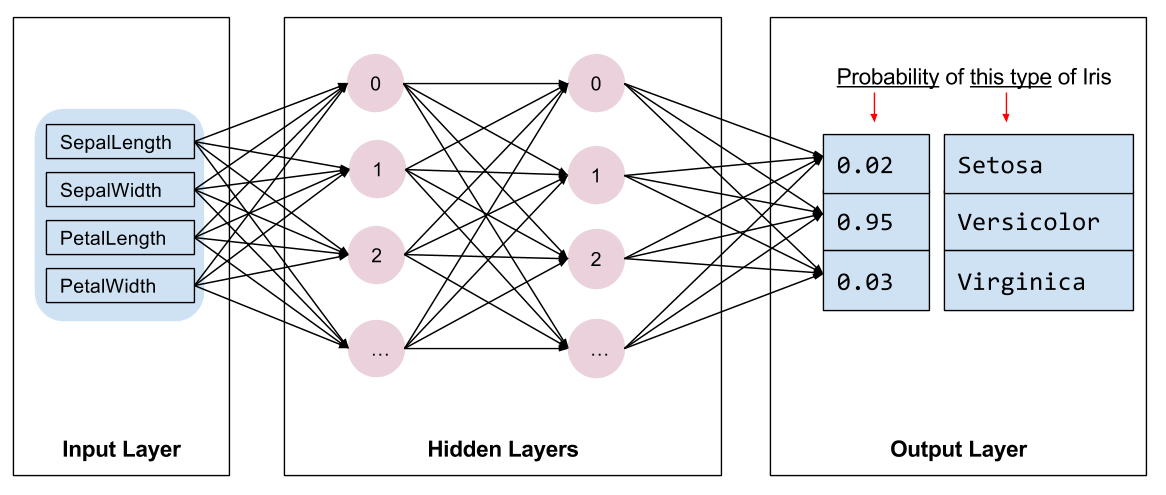
Figure 2. A fully-connected neural network consisting of an input layer (features), two hidden layers, and an output layer (predictions). |
// Import Swift for TensorFlow Deep Learning Library
import Tensorflow
import Pythonkit
import Python
/** Define a neural network
We'll define a neural network that is three layers:layer1 = features -> size(hidden_nodes)
layer2 = size(hidden_nodes) -> size(hidden_nodes)
layer3 = size(hidden_nodes) -> p(features) = {labels}
**/
// Set the # of artificial neurons
let hiddenSize: Int = 10
// Implement a model: fully-connected Neural Network (NN)
struct lightIrisModel: Layer {
var layer1 = Dense<Float>(inputSize: 4, outputSize: hiddenSize, activation: relu)
var layer2 = Dense<Float>(inputSize: hiddenSize, outputSize: hiddenSize, activation: relu)
var layer3 = Dense<Float>(inputSize: hiddenSize, outputSize: 3)
// Differentiable Programming!
@differentiable
func callAsFunction(_ input: Tensor<Float>) -> Tensor<Float> {
return input.sequenced(through: layer1, layer2, layer3)
}
}
Reinforcement Learning in Swift (Cart-Pole, The Classic Control Example)
// Copyright 2019, Emmanouil Antonios Platanios. All Rights Reserved.
//
// Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not
// use this file except in compliance with the License. You may obtain a copy of
// the License at
//
// http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
//
// Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
// distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT
// WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the
// License for the specific language governing permissions and limitations under
// the License.
import TensorFlow
@usableFromInline internal let gravity: Float = 9.8
@usableFromInline internal let cartMass: Float = 1.0
@usableFromInline internal let poleMass: Float = 0.1
@usableFromInline internal let length: Float = 0.5
@usableFromInline internal let forceMagnitude: Float = 10.0
@usableFromInline internal let secondCountBetweenUpdates: Float = 0.02
@usableFromInline internal let angleThreshold: Float = 12 * 2 * Float.pi / 360
@usableFromInline internal let positionThreshold: Float = 2.4
@usableFromInline internal let totalMass: Float = cartMass + poleMass
@usableFromInline internal let poleMassLength: Float = poleMass * length
public struct CartPoleEnvironment: RenderableEnvironment {
public let batchSize: Int
public let actionSpace: Discrete
public var observationSpace: ObservationSpace
@usableFromInline internal var step: Step<Observation, Tensor<Float>>
@usableFromInline internal var needsReset: Tensor<Bool>
@usableFromInline internal var renderer: CartPoleRenderer? = nil
@inlinable public var currentStep: Step<Observation, Tensor<Float>> { step }
@inlinable
public init(batchSize: Int, renderer: CartPoleRenderer? = nil) {
self.batchSize = batchSize
self.actionSpace = Discrete(withSize: 2, batchSize: batchSize)
self.observationSpace = ObservationSpace(batchSize: batchSize)
self.step = Step(
kind: StepKind.first(batchSize: batchSize),
observation: observationSpace.sample(),
reward: Tensor<Float>(ones: [batchSize]))
self.needsReset = Tensor<Bool>(repeating: false, shape: [batchSize])
self.renderer = renderer
}
/// Updates the environment according to the provided action.
@inlinable
@discardableResult
public mutating func step(taking action: Tensor<Int32>) -> Step<Observation, Tensor<Float>> {
// precondition(actionSpace.contains(action), "Invalid action provided.")
var position = step.observation.position
var positionDerivative = step.observation.positionDerivative
var angle = step.observation.angle
var angleDerivative = step.observation.angleDerivative
// Calculate the updates to the pole position, angle, and their derivatives.
let force = Tensor<Float>(2 * action - 1) * forceMagnitude
let angleCosine = cos(angle)
let angleSine = sin(angle)
let temp = force + poleMassLength * angleDerivative * angleDerivative * angleSine
let angleAccNominator = gravity * angleSine - temp * angleCosine / totalMass
let angleAccDenominator = 4/3 - poleMass * angleCosine * angleCosine / totalMass
let angleAcc = angleAccNominator / (length * angleAccDenominator)
let positionAcc = (temp - poleMassLength * angleAcc * angleCosine) / totalMass
position += secondCountBetweenUpdates * positionDerivative
positionDerivative += secondCountBetweenUpdates * positionAcc
angle += secondCountBetweenUpdates * angleDerivative
angleDerivative += secondCountBetweenUpdates * angleAcc
// Take into account the finished simulations in the batch.
let sample = observationSpace.sample()
step.observation.position = position.replacing(with: sample.position, where: needsReset)
step.observation.positionDerivative = positionDerivative.replacing(
with: sample.positionDerivative,
where: needsReset)
step.observation.angle = angle.replacing(with: sample.angle, where: needsReset)
step.observation.angleDerivative = angleDerivative.replacing(
with: sample.angleDerivative,
where: needsReset)
let newNeedsReset = (step.observation.position .< -positionThreshold)
.elementsLogicalOr(step.observation.position .> positionThreshold)
.elementsLogicalOr(step.observation.angle .< -angleThreshold)
.elementsLogicalOr(step.observation.angle .> angleThreshold)
step.kind.rawValue = Tensor(onesLike: step.kind.rawValue)
.replacing(with: Tensor<Int32>(zeros: newNeedsReset.shape), where: needsReset)
.replacing(with: 3 * Tensor<Int32>(ones: newNeedsReset.shape), where: newNeedsReset)
// Rewards need not be updated because they are always equal to one.
needsReset = newNeedsReset
return step
}
/// Resets the environment.
@inlinable
@discardableResult
public mutating func reset() -> Step<Observation, Tensor<Float>> {
step.kind = StepKind.first(batchSize: batchSize)
step.observation = observationSpace.sample()
needsReset = Tensor<Bool>(repeating: false, shape: [batchSize])
return step
}
/// Returns a copy of this environment that is reset before being returned.
@inlinable
public func copy() -> CartPoleEnvironment {
CartPoleEnvironment(batchSize: batchSize, renderer: renderer)
}
@inlinable
public mutating func render() {
if renderer == nil { renderer = CartPoleRenderer() }
renderer!.render(observation: step.observation)
}
}
extension CartPoleEnvironment {
public struct Observation: Differentiable, KeyPathIterable {
public var position: Tensor<Float>
public var positionDerivative: Tensor<Float>
public var angle: Tensor<Float>
public var angleDerivative: Tensor<Float>
@inlinable
public init(
position: Tensor<Float>,
positionDerivative: Tensor<Float>,
angle: Tensor<Float>,
angleDerivative: Tensor<Float>
) {
self.position = position
self.positionDerivative = positionDerivative
self.angle = angle
self.angleDerivative = angleDerivative
}
}
public struct ObservationSpace: Space {
public let distribution: ValueDistribution
@inlinable
public init(batchSize: Int) {
self.distribution = ValueDistribution(batchSize: batchSize)
}
@inlinable
public var description: String {
"CartPoleObservation"
}
@inlinable
public func contains(_ value: Observation) -> Bool {
true
}
public struct ValueDistribution: DifferentiableDistribution, KeyPathIterable {
@noDerivative public let batchSize: Int
public var positionDistribution: Uniform<Float> {
Uniform<Float>(
lowerBound: Tensor<Float>(repeating: -0.05, shape: [batchSize]),
upperBound: Tensor<Float>(repeating: 0.05, shape: [batchSize]))
}
public var positionDerivativeDistribution: Uniform<Float> {
Uniform<Float>(
lowerBound: Tensor<Float>(repeating: -0.05, shape: [batchSize]),
upperBound: Tensor<Float>(repeating: 0.05, shape: [batchSize]))
}
public var angleDistribution: Uniform<Float> {
Uniform<Float>(
lowerBound: Tensor<Float>(repeating: -0.05, shape: [batchSize]),
upperBound: Tensor<Float>(repeating: 0.05, shape: [batchSize]))
}
public var angleDerivativeDistribution: Uniform<Float> {
Uniform<Float>(
lowerBound: Tensor<Float>(repeating: -0.05, shape: [batchSize]),
upperBound: Tensor<Float>(repeating: 0.05, shape: [batchSize]))
}
@inlinable
public init(batchSize: Int) {
self.batchSize = batchSize
}
// TODO: @inlinable
@differentiable(wrt: self)
public func logProbability(of value: Observation) -> Tensor<Float> {
positionDistribution.logProbability(of: value.position) +
positionDerivativeDistribution.logProbability(of: value.positionDerivative) +
angleDistribution.logProbability(of: value.angle) +
angleDerivativeDistribution.logProbability(of: value.angleDerivative)
}
// TODO: @inlinable
@differentiable(wrt: self)
public func entropy() -> Tensor<Float> {
positionDistribution.entropy() +
positionDerivativeDistribution.entropy() +
angleDistribution.entropy() +
angleDerivativeDistribution.entropy()
}
@inlinable
public func mode() -> Observation {
Observation(
position: positionDistribution.mode(),
positionDerivative: positionDerivativeDistribution.mode(),
angle: angleDistribution.mode(),
angleDerivative: angleDerivativeDistribution.mode())
}
@inlinable
public func sample() -> Observation {
Observation(
position: positionDistribution.sample(),
positionDerivative: positionDerivativeDistribution.sample(),
angle: angleDistribution.sample(),
angleDerivative: angleDerivativeDistribution.sample())
}
}
}
}
public struct CartPoleRenderer: GLFWScene {
public let windowWidth: Int
public let windowHeight: Int
public let worldWidth: Float
public let scale: Float
public let cartTop: Float
public let poleWidth: Float
public let poleLength: Float
public let cartWidth: Float
public let cartHeight: Float
@usableFromInline internal var window: GLFWWindow
@usableFromInline internal var cart: GLFWGeometry
@usableFromInline internal var pole: GLFWGeometry
@usableFromInline internal var axle: GLFWGeometry
@usableFromInline internal var track: GLFWGeometry
@usableFromInline internal var cartTransform: GLFWTransform
@usableFromInline internal var poleTransform: GLFWTransform
@inlinable
public init(
windowWidth: Int = 600,
windowHeight: Int = 400,
positionThreshold: Float = 2.4,
cartTop: Float = 100.0,
poleWidth: Float = 10.0,
cartWidth: Float = 50.0,
cartHeight: Float = 30.0
) {
self.windowWidth = windowWidth
self.windowHeight = windowHeight
self.worldWidth = positionThreshold * 2
self.scale = Float(windowWidth) / worldWidth
self.cartTop = cartTop
self.poleWidth = poleWidth
self.poleLength = scale
self.cartWidth = cartWidth
self.cartHeight = cartHeight
// Create the GLFW window along with all the shapes.
self.window = try! GLFWWindow(
name: "CartPole Environment",
width: windowWidth,
height: windowHeight,
framesPerSecond: 60)
let (cl, cr, ct, cb) = (
-cartWidth / 2, cartWidth / 2,
cartHeight / 2, -cartHeight / 2)
self.cart = GLFWPolygon(vertices: [(cl, cb), (cl, ct), (cr, ct), (cr, cb)])
self.cartTransform = GLFWTransform()
self.cart.attributes.append(cartTransform)
let (pl, pr, pt, pb) = (
-poleWidth / 2, poleWidth / 2,
poleLength - poleWidth / 2, -poleWidth / 2)
self.pole = GLFWPolygon(vertices: [(pl, pb), (pl, pt), (pr, pt), (pr, pb)])
self.pole.attributes.append(GLFWColor(red: 0.8, green: 0.6, blue: 0.4))
self.poleTransform = GLFWTransform(translation: (0.0, cartHeight / 4))
self.pole.attributes.append(poleTransform)
self.pole.attributes.append(cartTransform)
let axleVertices = (0..<30).map { i -> (Float, Float) in
let angle = 2 * Float.pi * Float(i) / Float(30)
return (cos(angle) * poleWidth / 2, sin(angle) * poleWidth / 2)
}
self.axle = GLFWPolygon(vertices: axleVertices)
self.axle.attributes.append(poleTransform)
self.axle.attributes.append(cartTransform)
self.axle.attributes.append(GLFWColor(red: 0.5, green: 0.5, blue: 0.8))
self.track = GLFWLine(start: (0.0, cartTop), end: (Float(windowWidth), cartTop))
self.track.attributes.append(GLFWColor(red: 0, green: 0, blue: 0))
}
@inlinable
public func draw() {
cart.renderWithAttributes()
pole.renderWithAttributes()
axle.renderWithAttributes()
track.renderWithAttributes()
}
@inlinable
public mutating func render(observation: CartPoleEnvironment.Observation) {
// TODO: Support batched environments.
let position = observation.position[0].scalarized()
let angle = observation.angle[0].scalarized()
cartTransform.translation = (position * scale + Float(windowWidth) / 2, cartTop)
poleTransform.rotation = -angle
render(in: window)
}
}
. . . To be continued